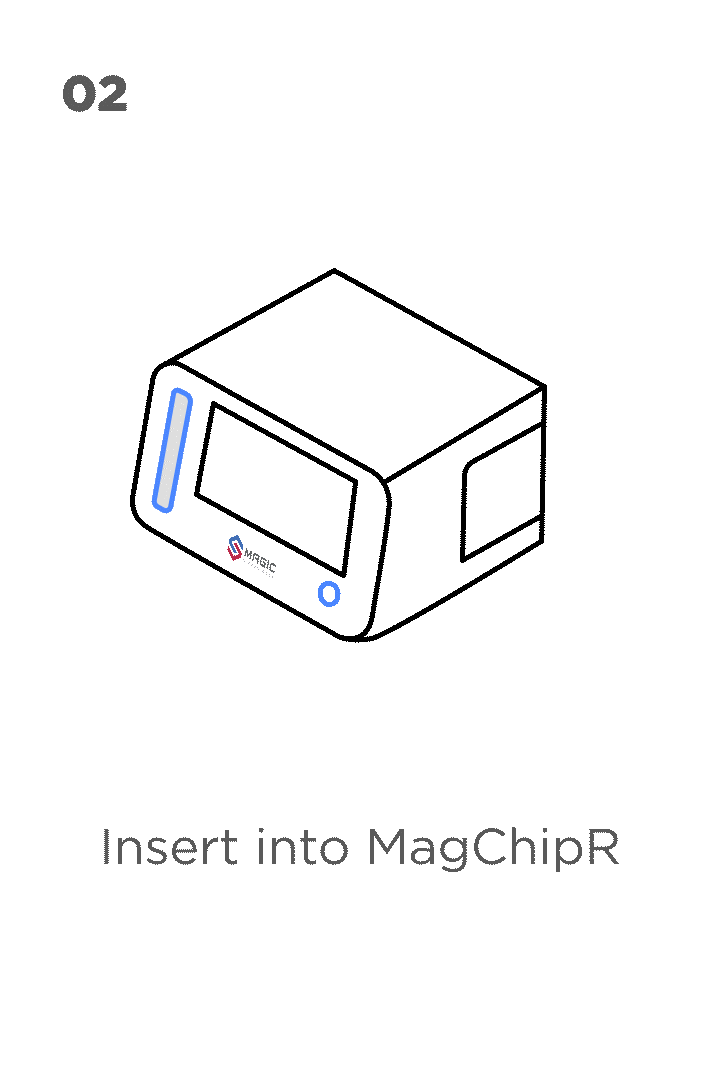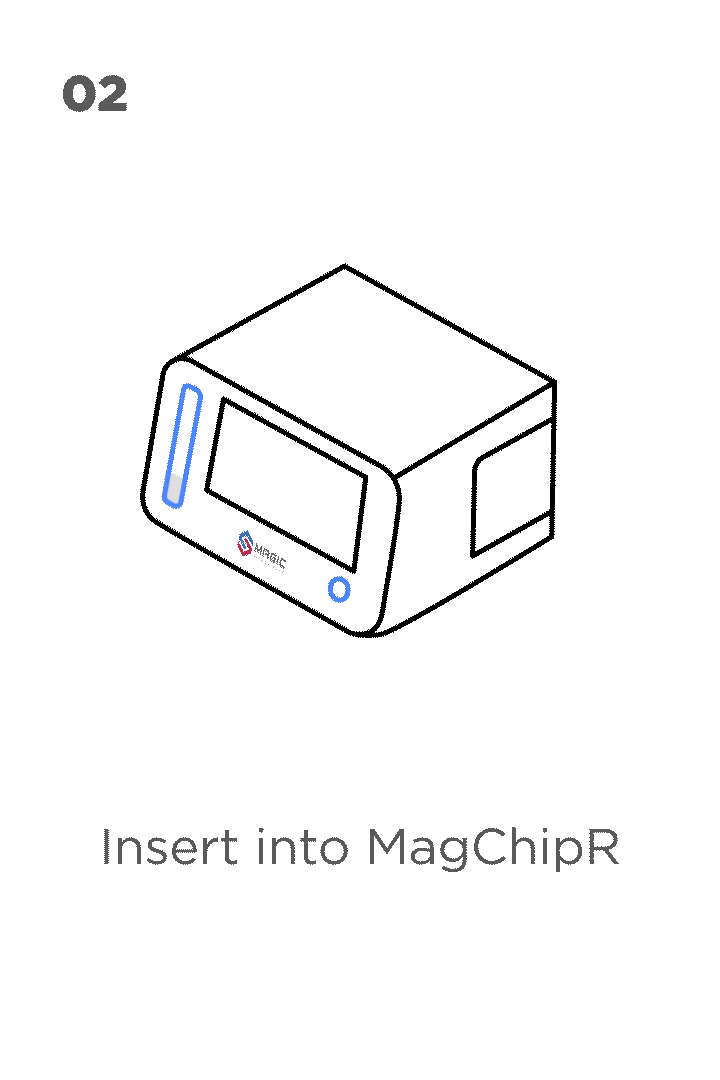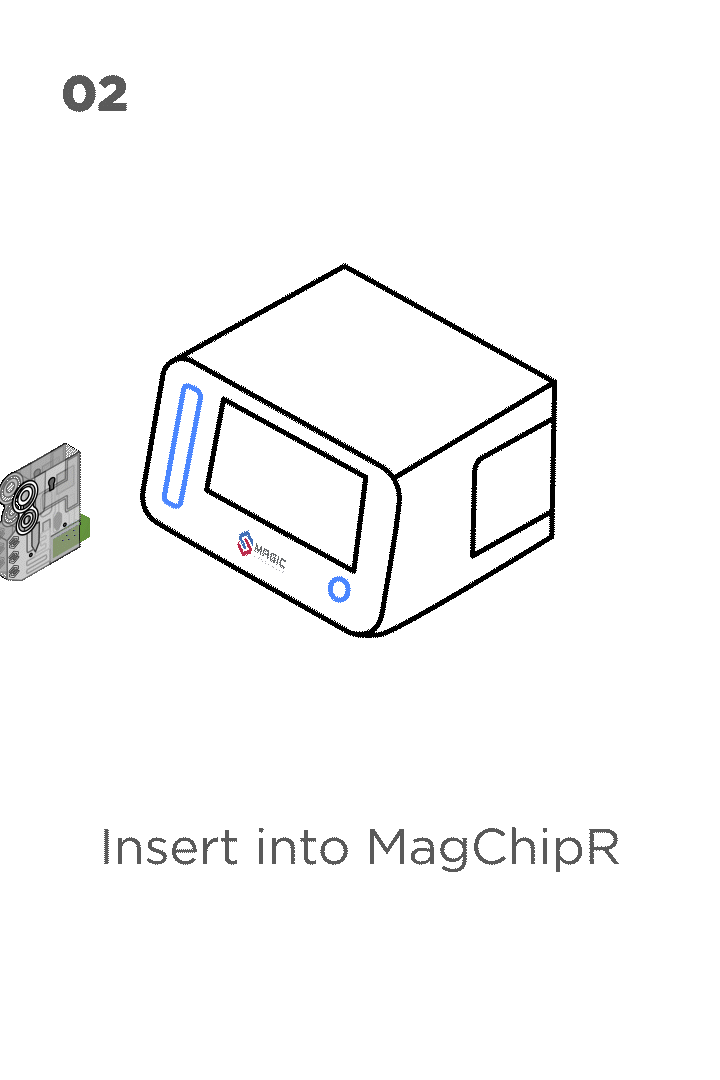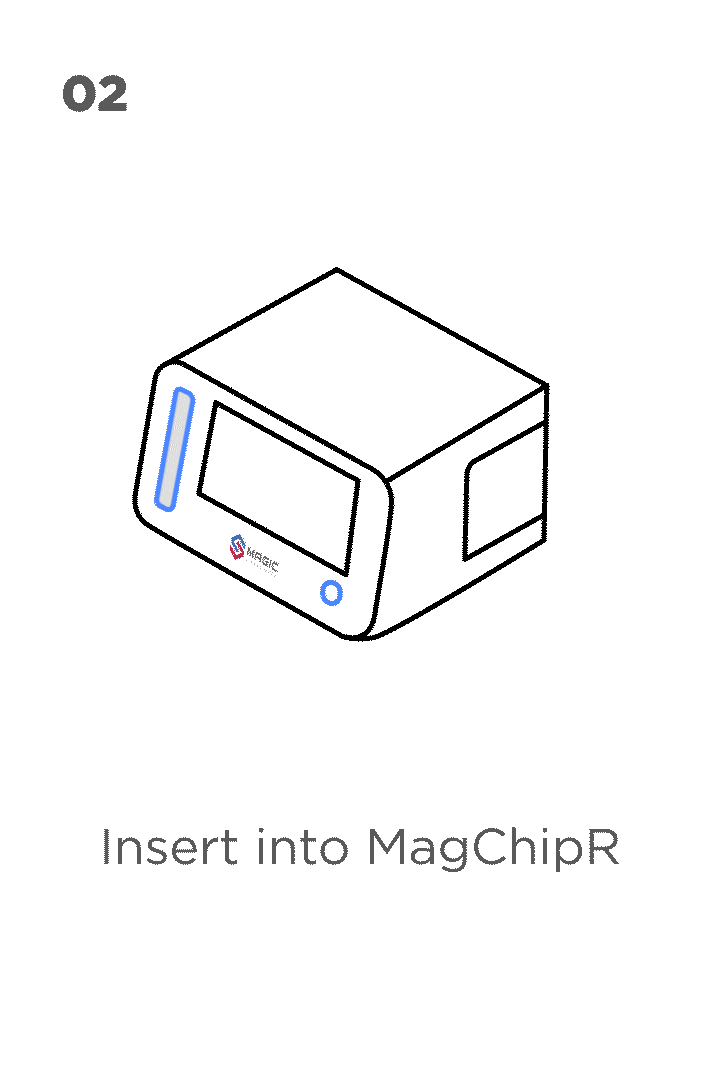
Chlamydia trachomatis
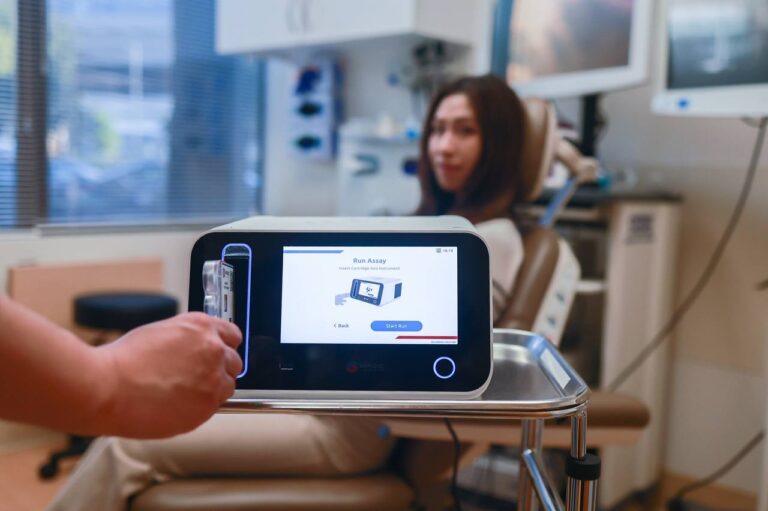
Chlamydia is the most common STI globally¹. Most people are unaware they have chlamydia, as the majority of infections are asymptomatic. Rapid diagnosis and treatment is critical to prevent pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), ectopic pregnancy, and infertility.
¹ Global Health Sector Strategy on Sexually Transmitted Infections, 2022-2030